Arg-Antibody Elution Buffer (pH 4.0)
This product leads to effective elution of antibodies from protein A columns under mild pH (pH 4.0). Normally, antibodies are not effectively eluted at pH 4.0. Use of a lower pH can lead to partial denaturation and subsequent aggregation of the eluted antibodies. This product is based on the unique characteristics of arginine, which suppresses protein-protein interactions.
This product is manufactured with permission from Ajinomoto Co., Inc. based on the patent JP 4826995*.
*JP: 4826995, US: 8084032, 8435527, 2012-0264918, EP: 1568710, CN: 1680426
Features
- Enables effective elution of antibodies from protein A column, reducing potential risk of acid denaturation and resultant aggregation
- Virus inactivation, a key step of clinical antibody manufacturing, is enhanced by arginine
- The use of this product has no impact on the preceding processes of antibody purification, e.g., loading step of cell culture medium and the following column washing step
- Arginine-based elution buffers are available in different formats upon request
Elution from Protein A using L-Arginine
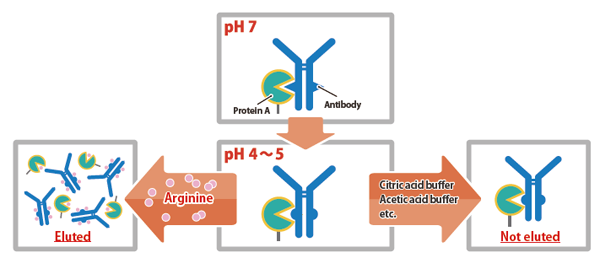
Applications
Example: Comparison with glycine-HCl elution buffer
Procedure
- Equilibrate protein A column (here COSMOGEL Ig-Accept Protein A) with D-PBS
- Load human serum
- Wash with 10 column volumes of D-PBS
- Elute with 5 volumes of acid (0.1 M glycine pH 2.8 - 4.0) or Arg-Antibody Elution Buffer
- Analyze eluted fractions, e.g., by SDS-PAGE
Results
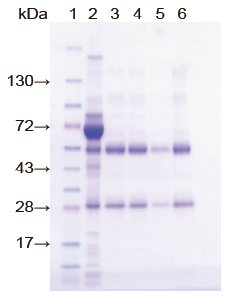
Arg-Antibody elution buffer shows much higher recovery (lane 6) than glycine buffer (lane 5).
Lane 1: Molecular weight marker (#09547-74)
Lane 2: Serum
Lane 3: 0.1 M Gly pH 2.8
Lane 4: 0.1 M Gly pH 3.4
Lane 5: 0.1 M Gly pH 4.0
Lane 6: Arg-Antibody Elution Buffer
Note that lanes 3, 4, 5 and 6 are independent results of the above procedure using
different elution buffers.
Protocols
Purification of antibody on Protein A column
- Equilibrate a protein A column with an appropriate buffer.
- Load a sample expressing antibodies.
- Wash the column with an appropriate buffer.
- Elute antibody with 5-10 column volumes of Arg-Antibody Elution Buffer.
- If necessary, perform virus inactivation taking advantage of enhanced virus inactivation by arginine.
- Proceed to next step, e.g., additional chromatography or buffer-exchange.
Cation exchange chromatography of the above eluted sample
- Equilibrate an appropriate cation exchange column with acetate buffer. The pH of the acetate buffer should be determined by the pI value of the antibody.
- Dilute the above eluate with 2-3 volumes of an appropriate acetate buffer.
- Load the diluted sample.
- Wash the column with an appropriate acetate buffer. The components of Arg-Antibody Elution Buffer are completely washed out in this process.
- Elute the antibody using high salt concentration, pH changes, or combination of both.
Arg-Antibody Elution Buffer (pH 4.0) Procedure ![]() (PDF 99 KB)
(PDF 99 KB)
Potential applications
As Arg-Antibody Elution Buffer can effectively weaken protein-protein interactions, there are a few additional applications of this product.
- Antigen-antibody affinity chromatography
- Dye chromatography
- Ligand chromatography
Downloads
Arg-Antibody Elution Buffer (pH 4.0)![]() (PDF 600 KB)
(PDF 600 KB)
References
- Elution of antibodies from Protein-A column by aqueous arginine solutions. Protein Expression and Purification 36(2), 244-248 (2004).
- Effective elution of antibodies by arginine and arginine derivatives in affinity column chromatography. Analytical Biochemistry 345(2), 250-257 (2005).
- Role of arginine in protein refolding, solubilization, and purification. Biotechnology Progress 20(5), 1301-1308 (2004).
- Screening of effective column rinse solvent for Protein-A chromatography. Protein Expression and Purification 70(2),218-223 (2010).