DL-Amino Acid Labeling Kit
This product is an amino acid labeling kit for HPLC analysis. Due to their high polarity and insufficient UV absorbance, amino acids need to be labeled prior to HPLC. In addition, research on D-amino acids has recently been gaining prominence. With conventional labeling reagents, such as phenyl isothiocyanate and dansyl chloride, costly chiral columns are required. This product is designed to label amino acids without intensive labor and achieve chiral separation with achiral columns, such as C18.
- Simple protocol
- Chiral separation with C18 column
- Compatible with high-sensitivity MS analysis
- Labeled amino acids are highly stable
>> Read our paper published in Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry.
HPLC application
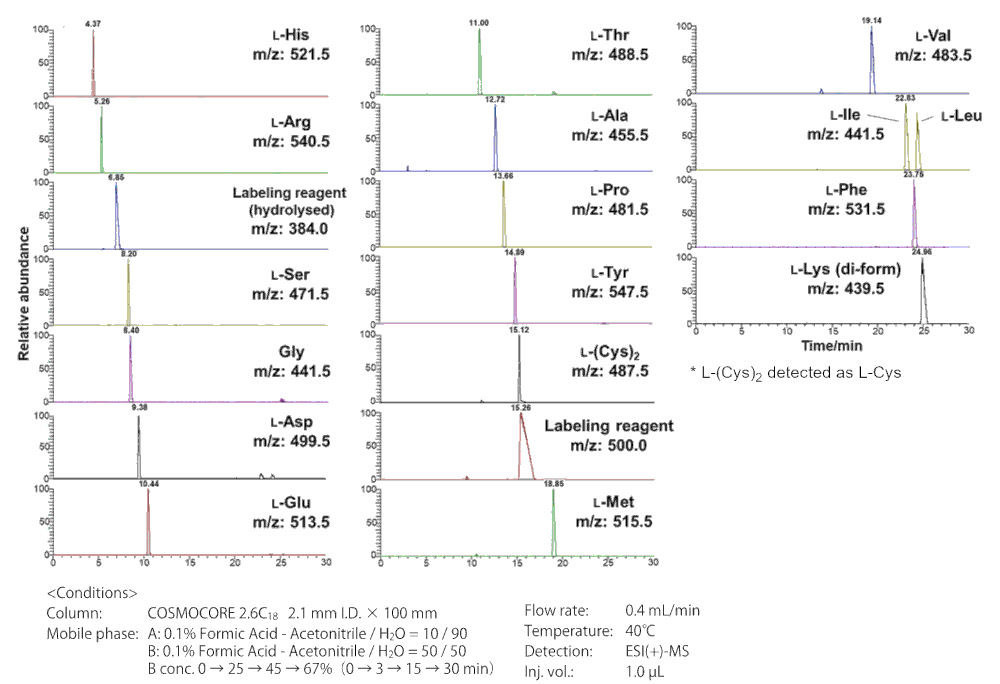
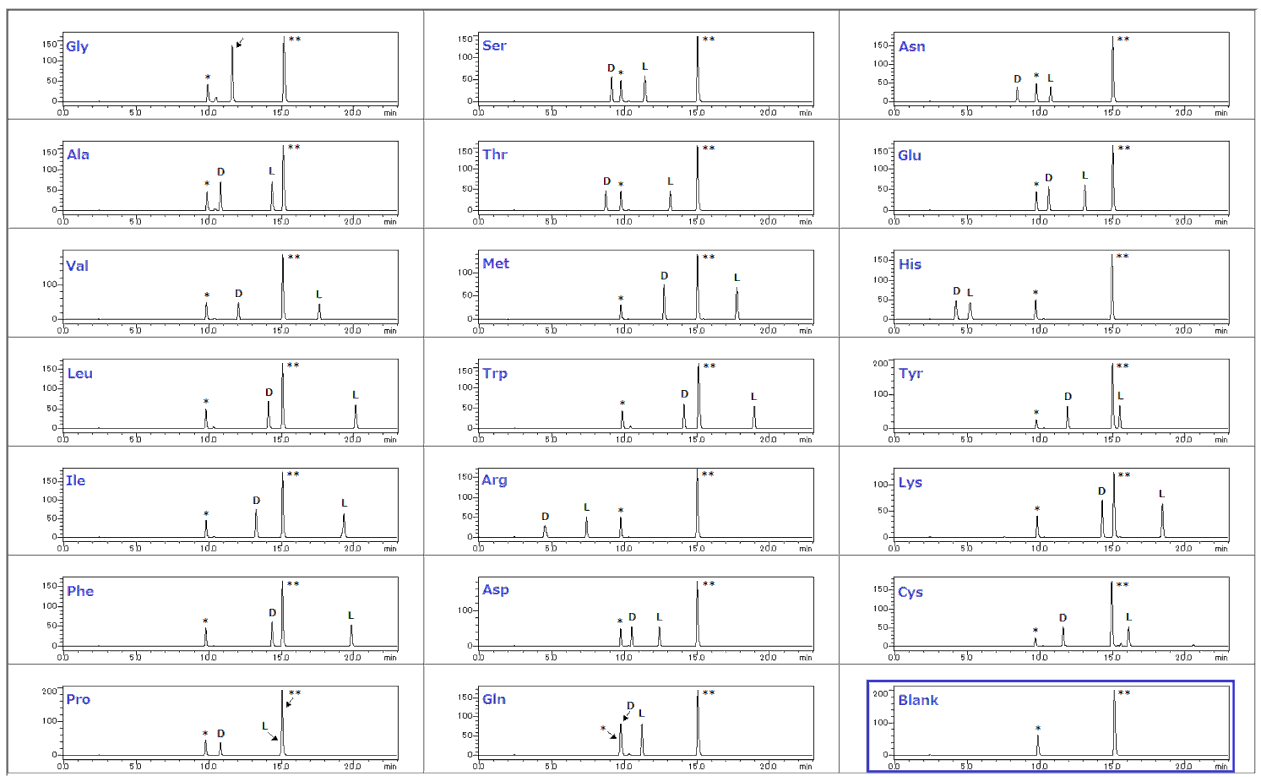
DL-amino acid separation by LC-MS (protocol 1)
19 DL-amino acids are separable (glycine is achiral).
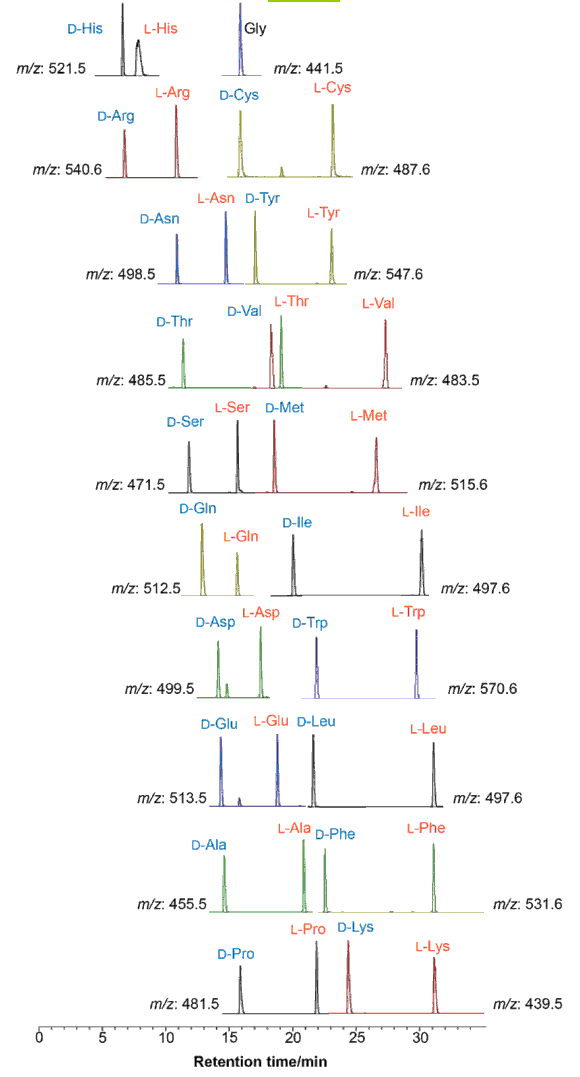
| Conditions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Column | COSMOCORE 2.6C18 2.1 mm I.D. x 100 mm | Flow rate | 0.4 mL/min |
| Mobile phase | A: 0.1 % Formic Acid - Acetonitrile = 10/90 B: 0.1 % Formic Acid - Acetonitrile = 50/50 B conc. 0 → 10% → 60% → 100% (0 → 5 → 30 → 35 min.) |
Temperature | 40°C |
| Detection | ESI(+)-MS | ||
| Sample | (DL)Amino Acid-(D)DLDA derivatives | ||
Kit components
| Name | PKG size | Required volume / assay |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sample*1 | User-supplied | 100 μL |
| 2 | Labeling solution*2 | 10 mL | 100 μL |
| 3 | Initiator solution | 10 mL | 100 μL |
| 4 | Delabeling solution (for side chain)*3 |
10 mL | 100 μL |
| 5 | Stop solution | 10 mL | 100 μL |
| 6 | Methanol or acetonitrile | User-supplied | 500 μL or 600 μL |
*1 Total amount of functional groups to be reacted should be less than 1.0 μmol. If higher, dilute or reduce sample amount.
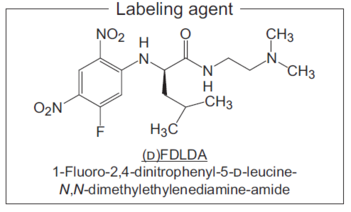
*2 Uses (D)FDLDA as the labeling reagent.
*3 Contains 6-mercapto-1-hexanol [M.W.: 134.24 (C6H14OS)]
Protocol
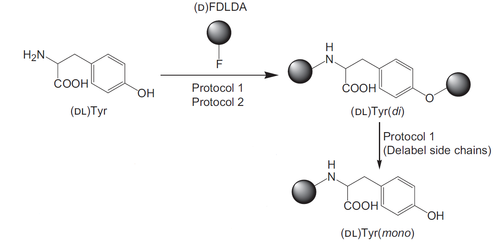
Two protocols are available
The labeling reagent reacts with amino groups. In addition, some side chains, such as the phenolic hydroxyl group of tyrosine and the thiol group of cysteine, are also labeled. Protocol 1 (step 2) achieves removal of labeling agents on side chains (except for Lys).
Protocol 1
Step 1:Add 100 µL each of sample solution, labeling agent solution, and start solution to a glass vessel, seal the vessel, mix in a vortex mixer for 5 seconds, and then react at 50°C for 2 hours.
Step 2:Add 100 µL of the delabeling agent solution for side chain, mix in a vortex mixer for 5 seconds, and then react at 50°C for 15 minutes.
Step 3:Add 100 µL of stop solution and 500 µL of acetonitrile or methanol, then analyze by HPLC (after filtration, if necessary).
Protocol 2
Step 1:Add 100 µL each of sample solution, labeling agent solution, and start solution to a glass vessel, seal the vessel, mix in a vortex mixer for 5 seconds, and then react at 50°C for 2 hours.
Step 2:Add 100 µL of stop solution and 600 µL of acetonitrile or methanol, then analyze by HPLC (after filtration, if necessary).
| Amino acid | Protocol 1 | Protocol 2 |
| Tyr, Cys | mono | di |
| Lys | di | di |
| His | mono | Mixture of mono and di |
| Other amino acids | mono | mono |
mono: Only the amino group of the α-carbon is labeled.
di: In addition to the α-carbon, the functional groups on the side chains are also labeled.
Figure 1: HPLC peaks derived from labeling reagent
| Name | Molecular weight | Description |
|---|---|---|
| (D)FDLDA | 385.39 (C16H24FN5O5) | Unreacted labeling reagent (only appears with protocol 2) |
| (D)FDLDA(Hydrolysed) | 383.40 (C16H25N5O6) |
Hydrolysate of labeling reagent |
| (D)FDLDA-S-C6H12OH | 499.63 (C22H37N5O6S) | Reaction product of labeling reagent and delabeling reagent (only appears with protocol 1) |
It is strongly recommended that a blank analysis is performed prior to analyzing your sample.
Reference
Kuranaga, T.; Minote, M.; Morimoto, R.; Pan, C.; Ogawa, H.; Kakeya, H. Highly Sensitive Labeling Reagents for Scarce Natural Products. ACS Chem. Biol. 2020, 15(9), p. 2499-2506.
LC/MS application
Analysis of amino acid mixture
Amino acids from hydrolyzation of peptides were labeled and analyzed by LC-MS.
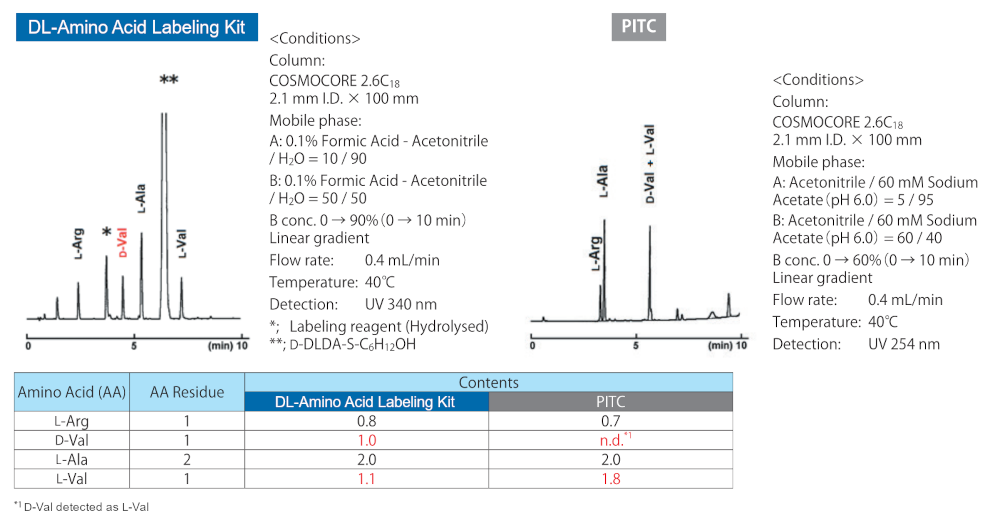
Analysis of hydrolyzed peptides (racemate)
A peptide with an L-form Val at the N terminal and a D-form Val in the center (H-VRVAA-NH2: LLDLL form) was hydrolyzed, and the amino acids obtained were labeled with the DL-Amino Acid Labeling Kit and PITC, which is commonly used for this purpose.
When using PITC, the D-Val and L-Val peaks completely overlap, making enantiomer quantification impossible. The sample labeled with DL-Amino Acid Labeling Kit resulted in distinct peaks for each enantiomer, enabling screening for racemized synthetic peptides.
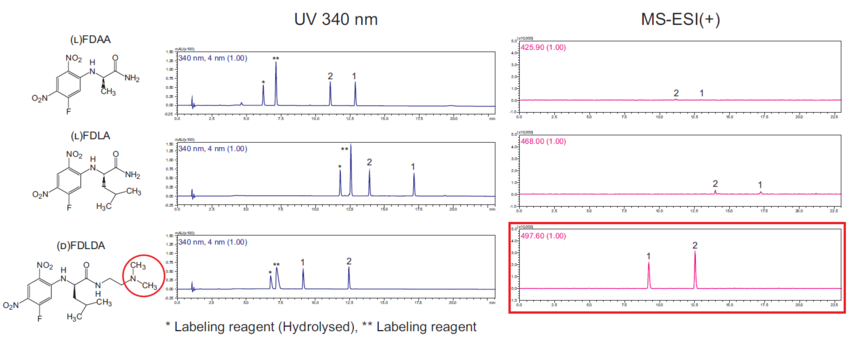
Comparison with other labeling reagents
For chiral separation of amino acids by achiral columns, (L)FDAA or (L)FDLA are well-known labeling reagents based on Marfey's method. This kit's labeling reagent (D)FDLDA is easily ionized at the red circle in the structure below, so MS sensitivity is higher compared to the conventional method, while UV sensitivity is about the same. Since the D-form labeling reagent is used, elution order is reversed compared to the conventional method.
Additional comparison data, including stability data, is also available.
| Condition | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Column | COSMOCORE 2.6C18 2.1 mm I.D. - 100 mm | Flow rate | 0.2 mL/min |
| Mobile phase | A: 0.1 % Formic Acid - 20 % Acetonitrile B: 0.1 % Formic Acid - 70 % Acetonitrile B conc. 0 → 100% 20 min linear gradient |
Temperature | 40°C |
| Detection | UV 340 nm, MS-ESI (+) | ||
| Sample | Labeled Leucine 1. D form 2. L form |
||
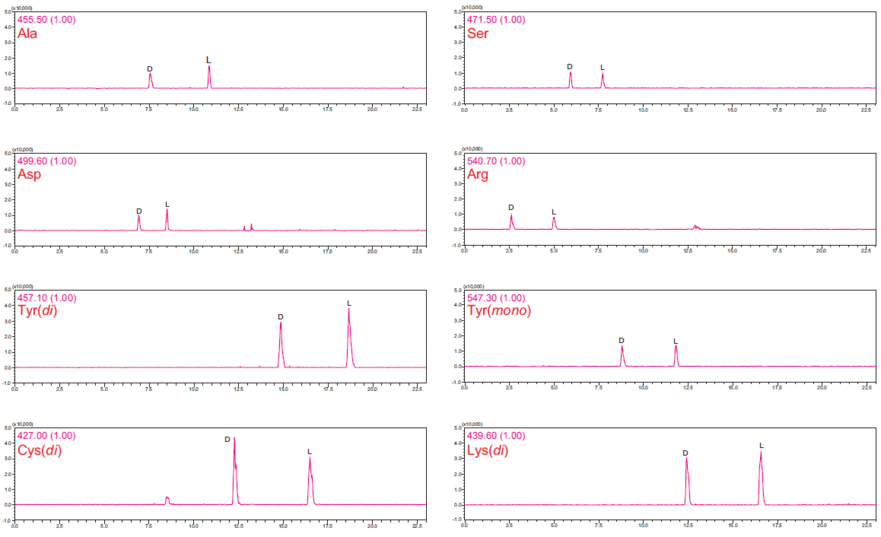
DL -amino acid separation (protocol 2)
| Condition | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Column | COSMOCORE 2.6C18 2.1 mm I.D. - 100 mm | Flow rate | 0.2 mL/min |
| Mobile phase | A: 0.1% Formic Acid - 20% Acetonitrile B: 0.1% Formic Acid - 50% Acetonitrile B conc. 0 → 100% 20 min linear gradient |
Temperature | 40°C |
| Detection | MS-ESI (+) | ||
| Sample | (DL)Amino Acid-(D)DLDA derivatives | ||
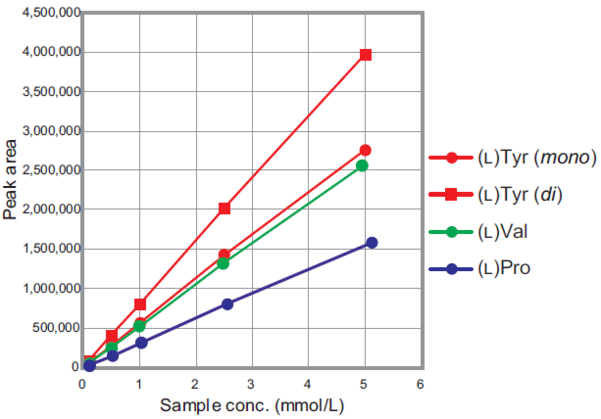
Quantitative performance
Calibration curve
Different concentrations of amino acids labeled with this kit were analyzed by HPLC. The calibration curve shows high linearity over the tested concentrations.
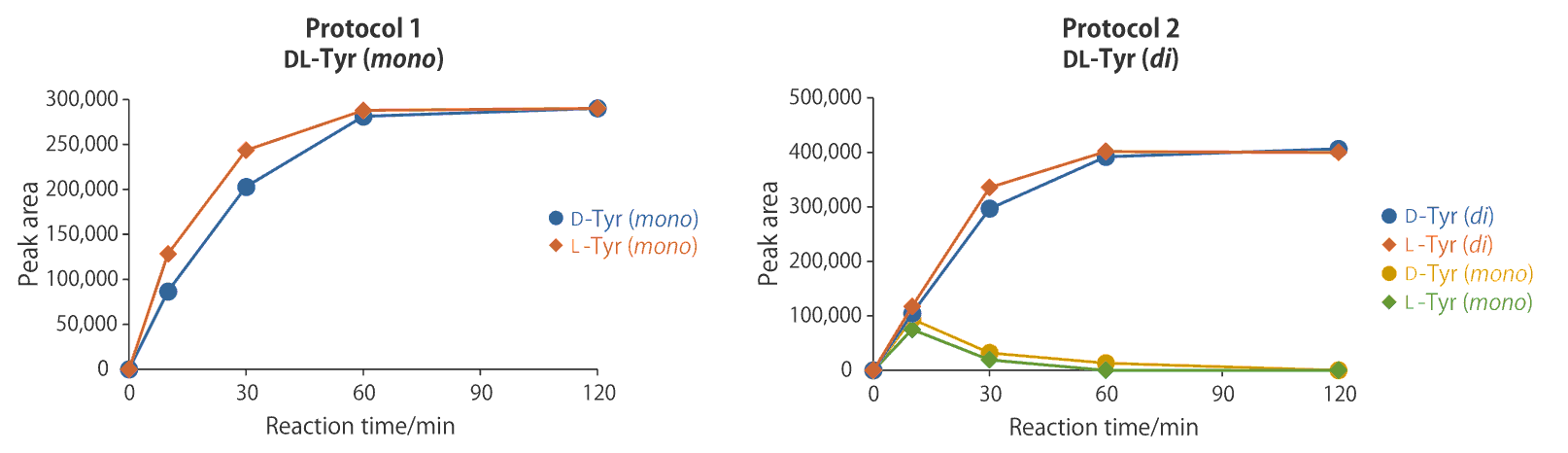
Labeling reaction
Protocol 1 : (L)Tyr (mono)
Protocol 2 : (L)Tyr (di), (L)Val, (L)Pro
Labeling reaction
Tyr has different numbers of labeling reagents depending on the protocol used. Upon observing the labeling reaction, it was found that the amino acid was completely labeled 2 hours after starting the reaction.
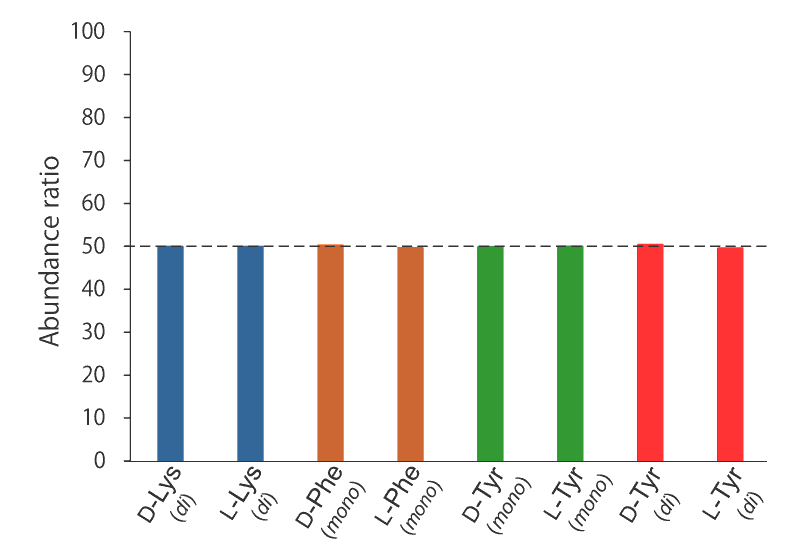
Ratio of labeled DL-amino acids
After reacting for 2 hours, the D/L ratio of the labeled amino acids was measured. It was confirmed that the amino acids are labeled precisely in a 1:1 ratio. In addition, D and L forms that were reacted separately had an enantiomeric excess (e.e.) of 100%.
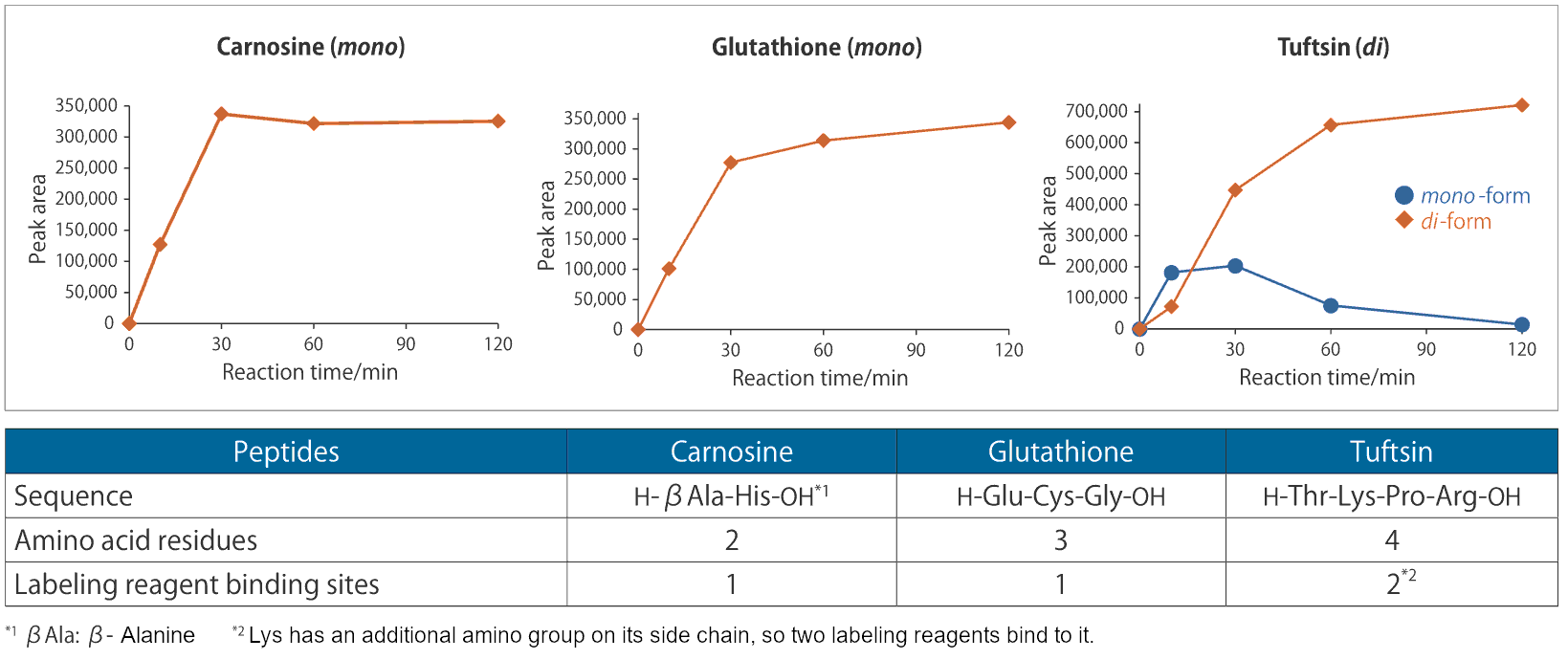
Labeling of peptides
In addition to amino acids, short-chain peptides can also be labeled.
Alternative selectivity with Cholester
Cholester offers alternative selectivity, which can resolve overlapping peaks caused by the labeling reagents. This can be useful for quantification with a UV detector.
When used together with a C18 column, the widest range of selectivity is achieved.
| Condition | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Column | COSMOSIL Cholester 4.6 mm I.D. x 150 mm | Flow rate | 1.0 mL/min |
| Mobile phase | A: 0.1 % Formic Acid - 20 % Acetonitrile B: 0.1 % Formic Acid - 50 % Acetonitrile B conc. 0 → 100% 20 min Linear gradient |
Temperature | 30°C |
| Detection | UV 340 nm | ||
| Sample | (DL)Amino Acid-(D)DLDA derivatives | ||
Other application data
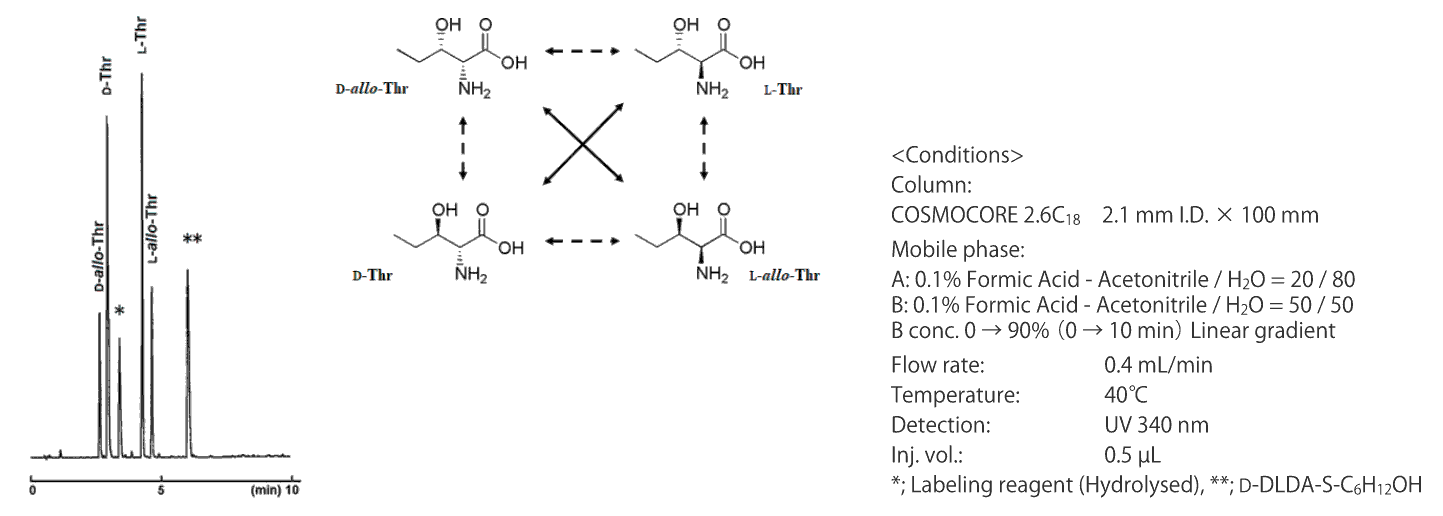
Separation of 4 isomers of Thr (HPLC, protocol 1)
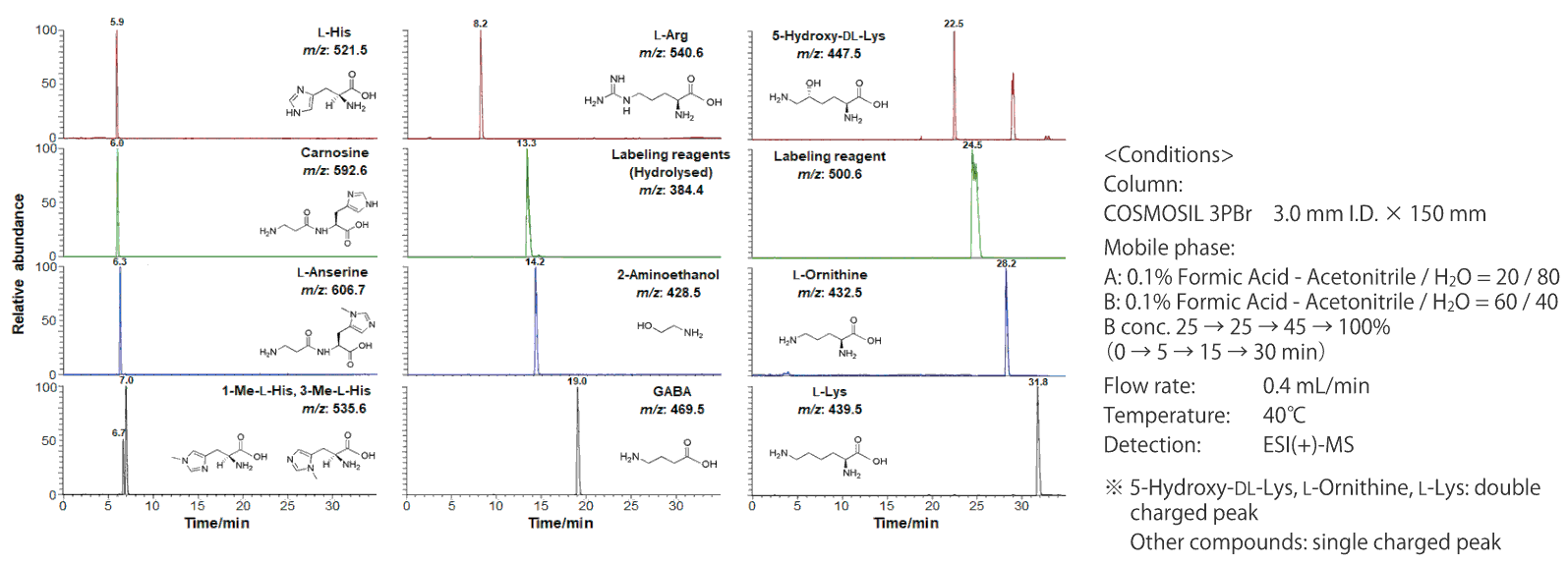
Separation of basic compounds (LC-MS, protocol 1)
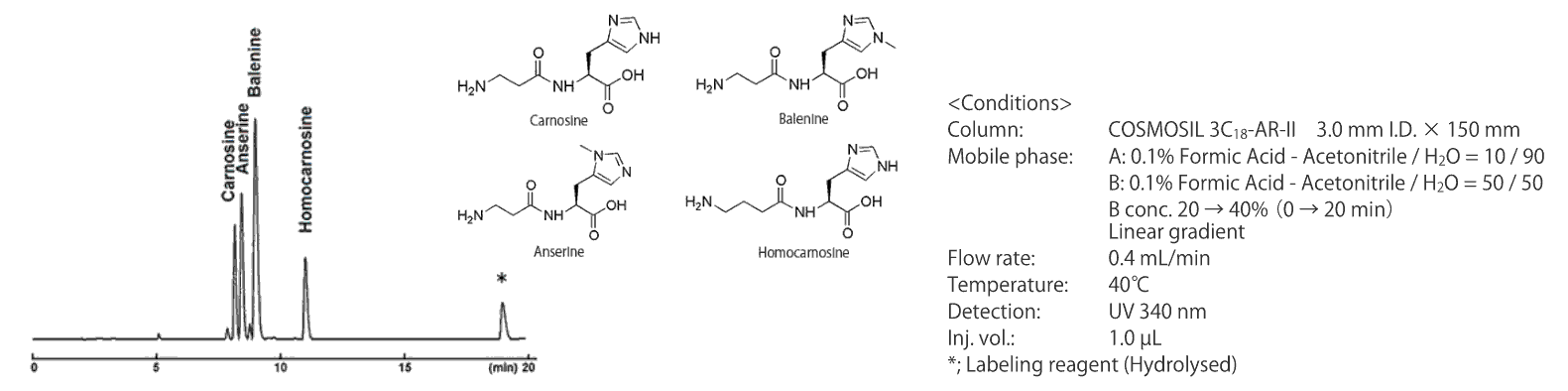
Separation of imidazole dipeptides (HPLC, protocol 1)
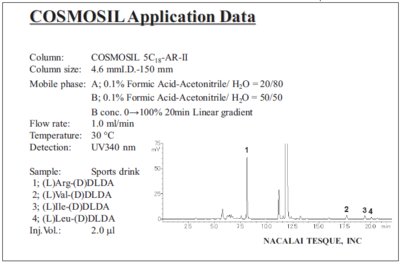
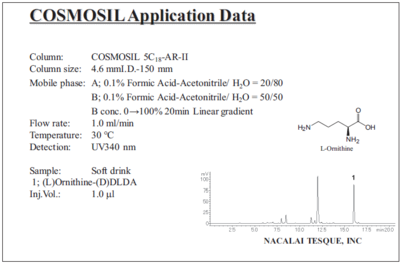
Commercial sports drink (protocol 2 with HPLC)
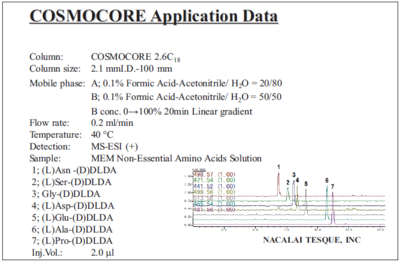
MEM non-essential amino acids solution (protocol 1 with LC/MS)
Commercial amino acid soft drink (protocol 2 with HPLC)
Histamine (protocol 1 with HPLC)
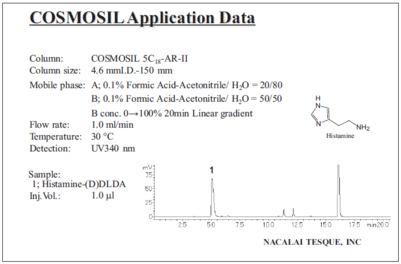
In addition to amino acids, this product is usable for other amine and thiol compounds.