HFIP for Nucleic Acid Analysis
1,1,1,3,3,3-Hexafluoro-2-propanol (HFIP) is frequently used as a mobile phase additive for analysis of oligonucleotides below 100 nucleotides (nt) and their impurities, due to the high sensitivity and separation it enables. However, there are significant differences in LC-MS sensitivity and even detection of unidentified peaks depending on the manufacturer, product grade, and lot. This product is specifically tested using LC-MS for each batch, so researchers can be confident in their reagents.
Features

- Suitable for analysis of oligonucleotides using HPLC and LC-MS
- Suitable for analysis of oligonucleotide impurities (short-mers, long-mers, phosphodiester [PO] impurities in phosphorothioated [PS] products)
- Each product lot tested using LC-MS
Performance comparison
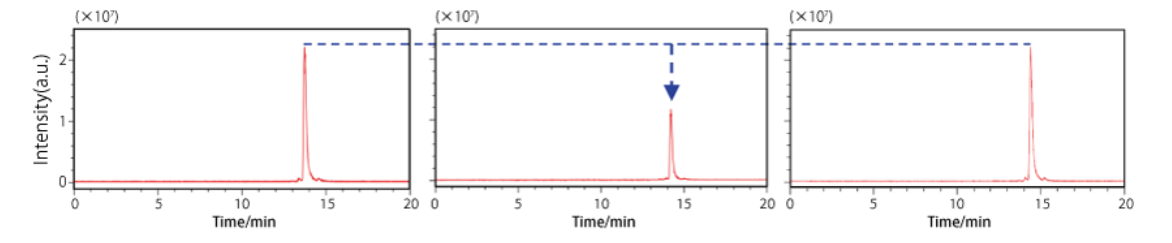
Using the oligonucleotide Poly(dT)19, LC-MS sensitivity was compared between this product and competitor HPLC and LC-MS grade products.
Nacalai Tesque product
Company A product
(HPLC grade)
Company B product (LC-MS grade)
| LC conditions | |
|---|---|
| Column | COSMOCORE 2.6C18 2.1 mm I.D. × 100 mm |
| Mobile phase | A : 100 mM HFIP-15 mM Triethylamine (TEA) B : Solvent A / Methanol = 1 / 1 (v / v) B conc. 20 → 50%(0 → 20 min) |
| Flow rate | 0.2 mL/min |
| Temperature | 40°C |
| MS conditions | |
|---|---|
| Equipment | LCMS 2050 (Shimadzu) |
| Ionization | ESI/APCI (Negative), TIC |
| Mode | Scan |
| Mass range | 550-2000 |
| Nebulizing gas flow | 2.0 L/min |
| Drying gas flow | 5.0 L/min |
| Heating gas flow | 7.0 L/min |
| DL temperature | 200°C |
| Desolvation temperature | 450°C |
| Interface voltage | -2.0 kV |
Compared to the company A product (HPLC grade), our product showed about twice the sensitivity. Additionally, it had about the same sensitivity as the company B product (LC-MS grade).
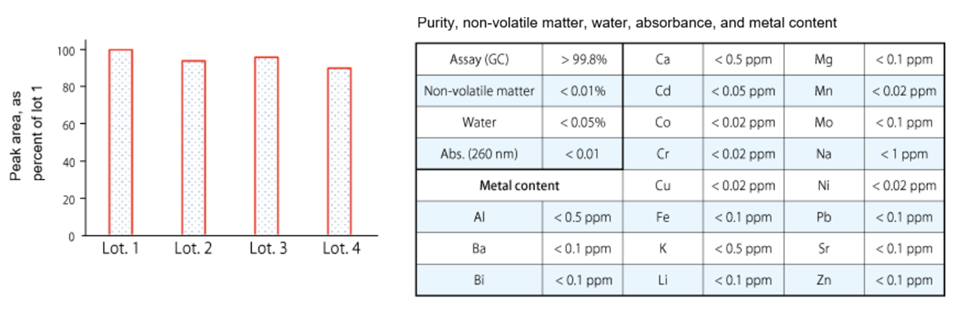
Comparing 4 different lots, the difference in sensitivity was found to be within 10%. Furthermore, there was no significant difference in purity and metal content.
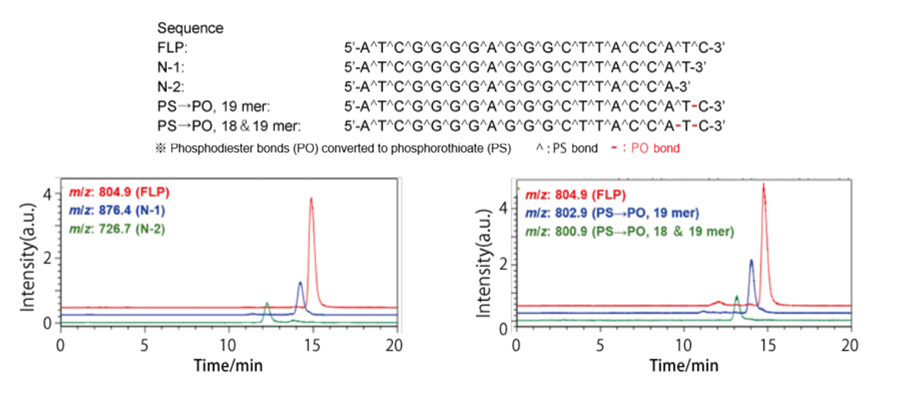
Analysis by LC-MS
Phosophorothioated oligonucleotides
By optimizing the analysis conditions, we were able to separate the target compound from impurities that are produced during synthesis.
| Conditions | |
|---|---|
| Column | COSMOCORE 2.6C18 2.1 mm I.D. × 100 mm |
| Mobile phase | A : 100 mM HFIP-15 mM Triethylamine (TEA) B : Solvent A / Acetonitrile / Methanol = 2 / 1 / 1 (v / v / v) B conc. 14 → 20%(0 → 20 min) |
| Flow rate | 0.2 mL/min |
| Temperature | 65°C |
| Ionization | ESI/APCI (Negative), SIM |
| Sample conc. | 100 µM (FLP) and 25 µM (others) |
| Inj. Vol. | 1 µL |
DNA ladder
Because hydrophobicity increases with oligonucleotide length, longer strands are retained for longer.
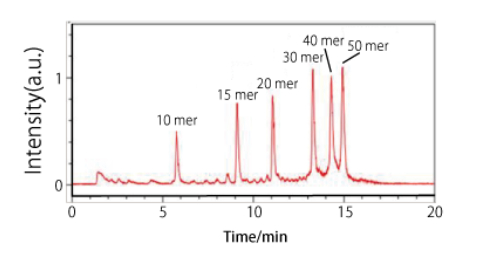
| Conditions | |
|---|---|
| Column | COSMOCORE 2.6C18 2.1 mm I.D. × 100 mm |
| Mobile phase | A : 100 mM HFIP-15 mM Triethylamine (TEA) B : Solvent A / Acetonitrile / Methanol = 2 / 1 / 1 (v / v / v) B conc. 7.5 → 27.5%(0 → 20 min) |
| Flow rate | 0.2 mL/min |
| Temperature | 65°C |
| Ionization | ESI/APCI (Negative), TIC |
| Sample conc. | 10 µM |
| Inj. Vol. | 3 µL |
ssDNA (PO and PS forms), ssRNA
Hydrophobicity increases in the order of RNA < DNA (PO) < DNA (PS), and the strands elute in the same order. Hydrophobicity also changes depending on the DNA sequence, so strands with similar length may have different retention times.
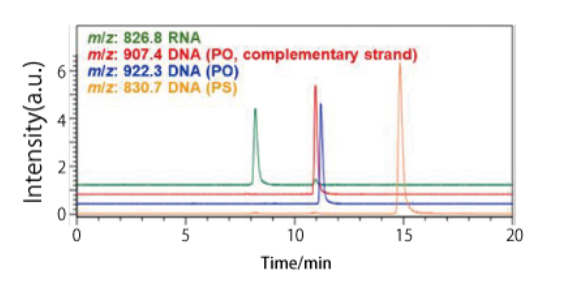
| Conditions | |
|---|---|
| Column | COSMOCORE 2.6C18 2.1 mm I.D. × 100 mm |
| Mobile phase | A : 100 mM HFIP-15 mM Triethylamine (TEA) B : Solvent A / Methanol = 1 / 1 (v / v) B conc. 20 → 60%(0 → 20 min) |
| Flow rate | 0.2 mL/min |
| Temperature | 40°C |
| Ionization | ESI/APCI (Negative), SIM |
| Sample conc. | Sample conc. |
| Inj. Vol. | 3 µL |
References
Separation and purification of short-, medium-, and long-stranded RNAs by RP-HPLC using different mobile phases and C18 columns with various pore sizes
Ozaki M, et al. Anal. Methods. 2024;16:1948-1956.
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4AY00114A
* Featured on Front Cover
Separation of long-stranded RNAs by RP-HPLC using an octadecyl-based column with super-wide pores
Kuwayama T, et al. Anal. Sci. 2023;39:417-425.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s44211-022-00253-w
* Selected as Hot Articles 2023
Ozaki M, et al. Medical Science Digest December Special Issue. 2023, 49, p.40-43.

Cover art on the front cover of Analytical Methods and the award certificate for being selected as one of the Hot Articles 2023.