Analysis of phosphorothioated DNA oligonucleotides
Oligonucleotide research has exploded in recent years, requiring new and sophisticated techniques not only in their application, but also analysis. Phosphorothioate modification of oligonucleotides (S-oligos) is a technique used to improve stability and slow degradation by nucleases. In the synthesis of S-oligos it is imperative that modifications are as directed, whether it be a partially or fully modified S-oligo. COSMOCORE C18 columns are shown here in a method to elucidate minute differences in chemical modification with excellent resolution.
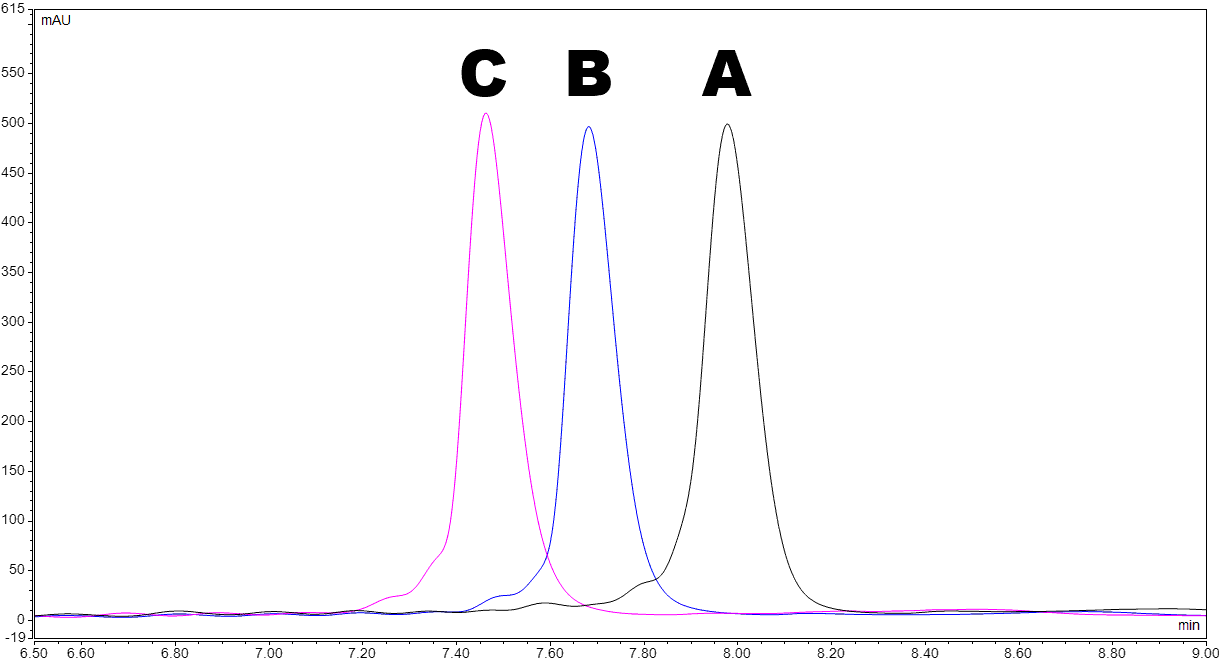
Figure 1: Overlaid chromatograms of fully and partially phosphorothioated DNA oligos. Excellent resolution is observed between oligos of the same length and differing number of modifications.
Acquisition method:
Column: COSMOCORE C18
Column Size: 2.1 x 100 mm
Mobile Phase: A: 100mM TEAA water; B: Acetonitrile
Gradient: 10 → 25 %B (0 → 10 min)
Flow Rate: 0.4 mL/min
Temperature: 50°C
Detection: UV 260
Sample: Phosphorothioate modified DNA oligos
Inj. Vol.: 1 µL
Sample sequences:
A: 20-mer All PS
T*T*T*T*T*T*T*T*T*T*T*T*T*T*T*T*T*T*T*T
B: 20-mer 1PO 5'
TT*T*T*T*T*T*T*T*T*T*T*T*T*T*T*T*T*T*T
C: 20-mer 2PO 5'+ middle
TT*T*T*T*T*T*T*T*T*TT*T*T*T*T*T*T*T*T
T* = phosphorothioate linkage
Data courtesy of Nacalai USA.