Analysis of Flavonoid Glycosides in Vegetables
Technical Note 22
In this note, flavonoids from vegetables were extracted and analyzed using a C18 column with UV and MS detection.
About flavonoids
Flavonoids are a type of polyphenol. The phenol hydroxy group has antioxidant effects, and these compounds are said to be able to prevent some lifestyle diseases.1 Tea catechins, onion quercetins,2 soy isoflavones, and hesperidin from citrus fruits3 are well-known examples; flavonoids are also found in plants such as buckwheat, other Fabaceae (bean family) plants, spinach,4,5 Apiaceae family plants including parsley,6 and Cruciferae family vegetables. With some exceptions, such as tea catechins, flavonoids mostly exist as glycosides.
Analysis of vegetable flavonoids with HPLC-UV
Onion bulb
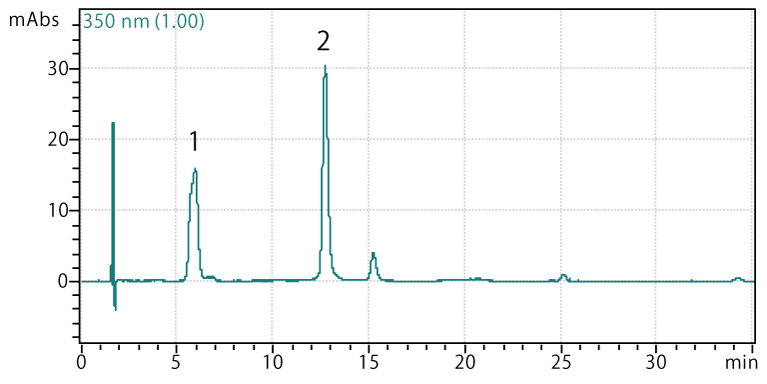
Sample: Onion bulb extract
Peaks:
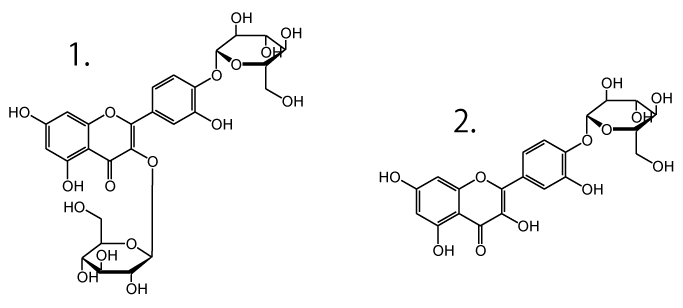
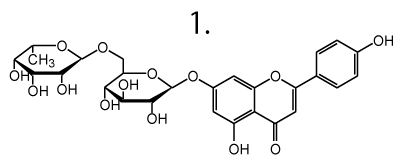
- Quercetin diglucoside
- Quercetin monoglucoside
Spinach leaf
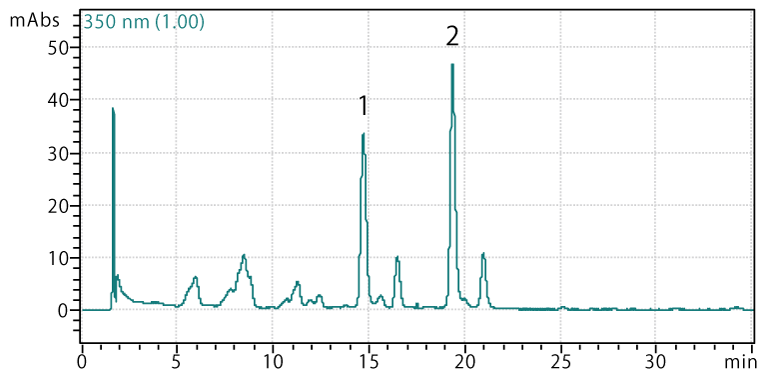
Sample: Spinach leaf extract
Peaks:
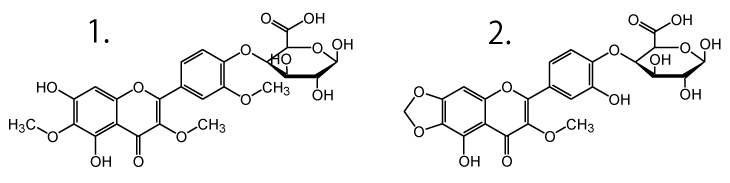
- Spinatoside monoglucuronide
- 5,3',4'-trihydroxy-3-methoxy-6:7-methylenedioxyflavone monoglucoside
Parsley leaf
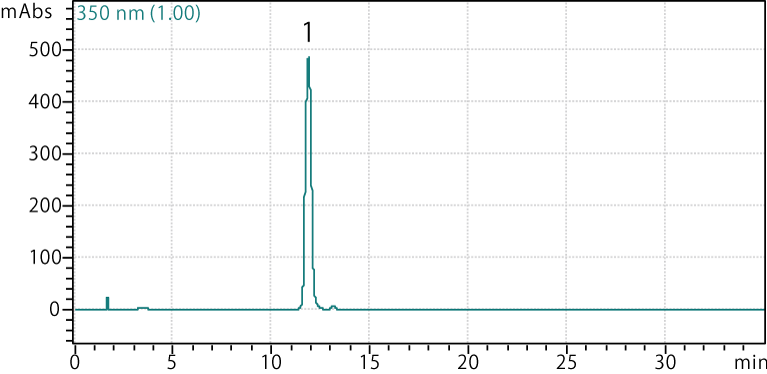
Sample: Parsley leaf extract
Peaks:
- Apigenin rutinoside
Analysis conditions
Column: COSMOSIL 2.5C18-MS-II, 2.0 mm I.D. × 150 mm
Mobile phase:
- A: 0.1% formic acid (MeOH:H2O = 10:90)
- B: 0.1% formic acid (MeOH:H2O = 90:10)
- B conc.
30%→60% (0 min.→25 min.),
60% (25 min.→30 min.),
60%→30% (30 min.→30.1 min.),
30% (30.1 min.→35 min.)
Flow rate: 0.2 mL/min
Temp.: 40°C
Detector: UV 350 nm
Injection vol.: 5 µL
Peaks were identified using LC-MS data and literature values.2,4,5,6
Sample extraction
- Vegetable preparation
- Onion bulb
Peel the brown skin off of the onion bulb, and chop the white edible portion finely with a knife. - Spinach leaf
Chop the spinach leaf finely with a knife. - Parsley leaf
Tear the parsley leaf from the stem and chop the leaf finely with a knife.
- Onion bulb
- Flavonoid extraction
- Mix the chopped vegetable well and measure 10 g for the sample.
- Add 80 mL of extraction solvent (MeOH:H2O = 80:20) and shake.
- Occasionally shake and stir with a glass rod, and leave overnight at room temperature.
- Filter using a Whatman grade 2 filter paper, and reserve the filtrate.
- Wash the residue by adding extraction solvent.
- Filter using a Whatman grade 2 filter paper, and mix the filtrate with that from step 4.
- Add extraction solvent to the liquid from step 6 to a total of 100 mL.
- Filter a portion using a Cosmonice Filter W, and use that as the HPLC sample.
Whatman is a registered trademark of Whatman International Ltd.
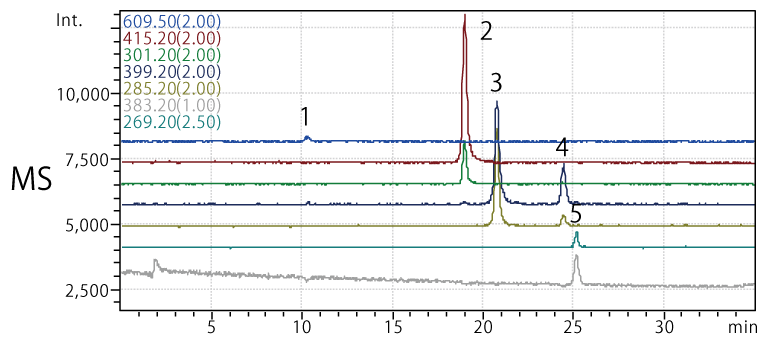
Analysis of standards by HPLC-MS
Column: COSMOSIL 2.5C18-MS-II, 2.0 mm I.D. × 150 mm
Mobile phase:
- A: 0.1% formic acid (MeOH:H2O = 10:90)
- B: 0.1% formic acid (MeOH:H2O = 90:10)
- B conc.
30%→60% (0 min.→25 min.),
60% (25 min.→30 min.),
60%→30% (30 min.→30.1 min.),
30% (30.1 min.→35 min.)
Flow rate: 0.2 mL/min
Temp.: 40°C
Detector: MS (ESI probe, MIC(-), M.W. for each sample)
Samples:
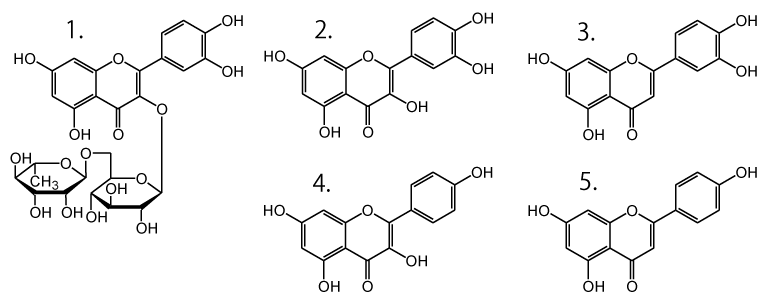
- Rutin (1 mg/mL, M.W. 610.5, m/z 609)
- Quercetin (1 mg/mL, M.W. 302.2, m/z 415*, 301)
- Luteolin (1 mg/mL, M.W. 286.2, m/z 399*, 285)
- Kaempferol (1 mg/mL, M.W. 286.2, m/z 399*, 285)
- Apigenin (1 mg/mL, M.W. 270.2, m/z 269, 383*)
* Trifluoroacetic acid adduct also detected.
Injection vol.: 0.25 µL each
References
- Inoue, J., Sato, R. KAGAKU TO SEIBUTSU. 2016, vol.54, no. 6, p. 416-420.
- Okamoto, D., et al. The Horticulture Journal. 2006, vol. 75, no. 1, p. 100-108.
- Nogata, Y. Bulletin of the National Agricultural Research Center for Western Region. 2005, vol. 5, p. 19-84.
- Watanabe, M., Ayugase, J. J. Sci. Food Agr. 2015, vol. 95, no. 10, p. 2095-2104.
- Watanabe, M., Ayugase, J. Food Science and Technology Research. 2015, vol. 62, no. 10, p. 501-507.
- Plazonic, A., et al. Molecules. 2009, vol. 14, no. 7, p. 2466-2490.